On This Page
What Are Zero-Emission Vehicles?
Zero-Emission Vehicles (ZEVs) are an important step toward reducing transportation-related emissions and building a sustainable future. These vehicles use alternative fuels (electricity or hydrogen) to substantially reduce greenhouse gas emissions and criteria air pollution during operation, offering cleaner alternatives to traditional gas-powered cars.
ZEVs include:
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)

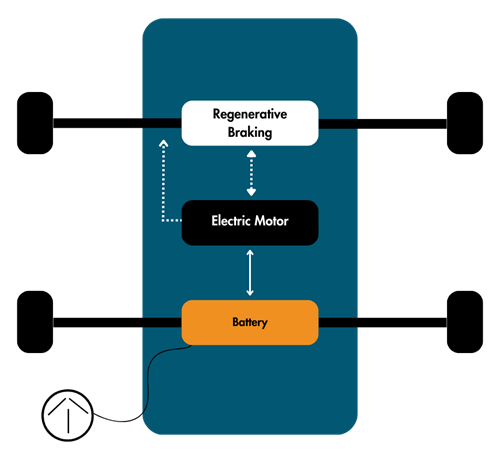
- Powered solely by electricity stored in a battery pack.
- Known as "true" or "full" EVs, with no onboard combustion.
- Uses lithium-ion batteries, like those in smartphones and laptops.
- They emit no pollutants and recharge through external electric sources or regenerative braking.
EV Charging Levels
Understanding EV charging options is key to seamless ZEV adoption. Charging levels vary by speed, voltage, and location:
| Charging Level | Power Type | Voltage | Charge Speed | Typical Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | Alternating Current (AC) | 120-volt | 3.5–6.5 miles per hour | Residences, some workplaces |
| Level 2 | Alternating Current (AC) | 208-/240-volt | 14–35 miles per hour | Residences, workplaces, public facilities |
| Level 3 | Direct Current (DC) | 480-volt | 10 miles per minute | Public facilities |
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs)

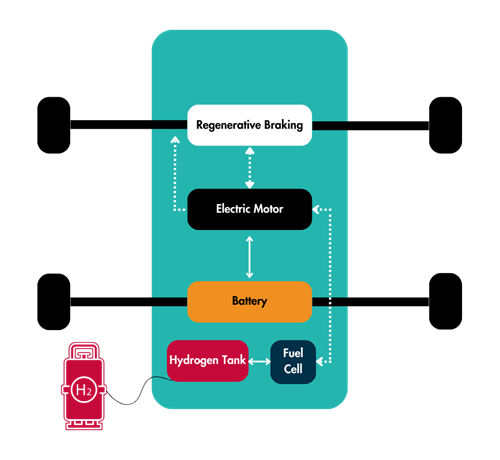
- Generate electricity using hydrogen, emitting only water vapor.
- Refuel quickly, similar to traditional methods.
- Provide clean, efficient zero-emission driving.
FCEV Refueling Levels
| Refueling Level | Power Type | Voltage | Refuel Time | Typical Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light-Duty FCEVs | Hydrogen (Gas) | High-pressure storage | 3–5 minutes | Hydrogen fueling stations |
| Heavy-Duty FCEVs | Hydrogen (Gas) | High-pressure storage | 15 minutes | Hydrogen fueling stations |
Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)

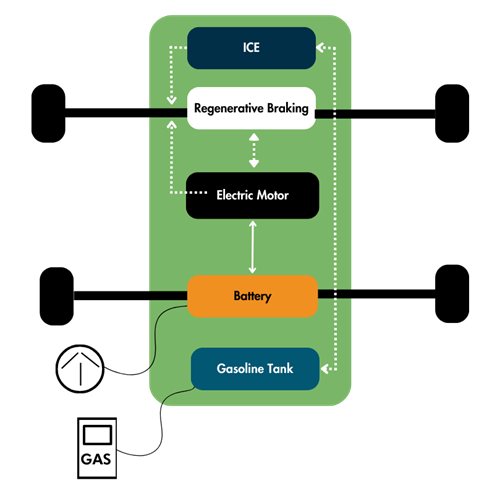
- Fueled by both electricity and gasoline.
- Run 15–50 miles on electricity before switching to gas.
- Combine an electric motor and a combustion engine.
PHEV Charging Levels
| Charging Level | Power Type | Voltage | Charge Speed | Typical Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | Alternating Current (AC) | 120-volt |
3.5–6.5 miles per hour |
Residences, some workplaces |
| Level 2 | Alternating Current (AC) | 208-/240-volt |
14–35 miles per hour |
Public facilities, workplaces |
Zero-Emission Vehicle Regional Study
Learn about different zero-emission vehicle technology types, explore regional trends and data, and find recommendations for future H-GAC activities supporting ZEV growth.
Explore H-GAC’s Regional EV Dashboard
This is your comprehensive tool for locating public charging stations and exploring the region’s EV infrastructure. Charge ahead and drive change to contribute to cleaner air with H-GAC’s Regional EV Dashboard. Explore the Full Dashboard.
Key features include:
 Map of existing public charging stations.
Map of existing public charging stations.
 Alternative fuel corridors with EV fast chargers every 50 miles.
Alternative fuel corridors with EV fast chargers every 50 miles.
 Planned charging stations and projects.
Planned charging stations and projects.
 Historic EV registration trends in the region.
Historic EV registration trends in the region.
Funding Opportunities
Ongoing efforts are driving the transition to a sustainable future.
Here's how these programs support ZEV adoption:

Purchase Incentives: Reducing costs for ZEV buyers.

Infrastructure Development: Expanding EV charging and hydrogen fueling stations.

Support for Hydrogen: $7 billion allocated to clean hydrogen hubs, including one in our region.



